Get to Know Our University
St. George’s University encompasses four schools—The School of Medicine, School of Veterinary Medicine, School of Arts and Sciences, and School of Graduate Studies.
1,049+
US residencies in 20 specialties in 2025.2 SGU is the largest source of actively licensed physicians in the entire US workforce.3
2) Data as of September 2025
3) According to FSMB physician licensure data, 2023.
School of Medicine
St. George’s University, an accredited Caribbean medical school, offers you three different term starts for maximum flexibility: August, January, and April. We are currently accepting applications for all three terms.
Learn first-hand about SGU’s School of Medicine as our diverse student body describes it in one word.
SGU offers flexible start terms in April 2026 so that you can pursue your dreams of becoming a doctor at a time that works best for you.
School of Veterinary Medicine
School of Arts and Sciences

Our School of Arts and Sciences helps you gain professional skills through undergraduate degree, dual-degree, and postbaccalaureate preclinical programs. You can apply your knowledge in internships and service-learning opportunities.
School of Graduate Studies

St. George’s University designed its graduate degree programs to keep pace with the evolving needs of business, public health, research, information science, and veterinary medical care.
Discover St. George's University
Life at SGU
Immerse yourself in a vibrant campus community, modern facilities, and supportive peers. Discover how SGU’s supportive campus community can shape your journey to becoming a physician.
Student Outcomes
Learn how our students do at securing residencies, succeed on USMLE exams, and advance their medical careers. View the data behind their success.
Attend An Event
Meet our admissions team, connect with recent graduates, and learn about our application process—online or in person.
Take a Virtual Tour
Explore academic facilities and wellness spaces designed to support your medical journey from day one.
Discover St. George's University



The SGU Difference
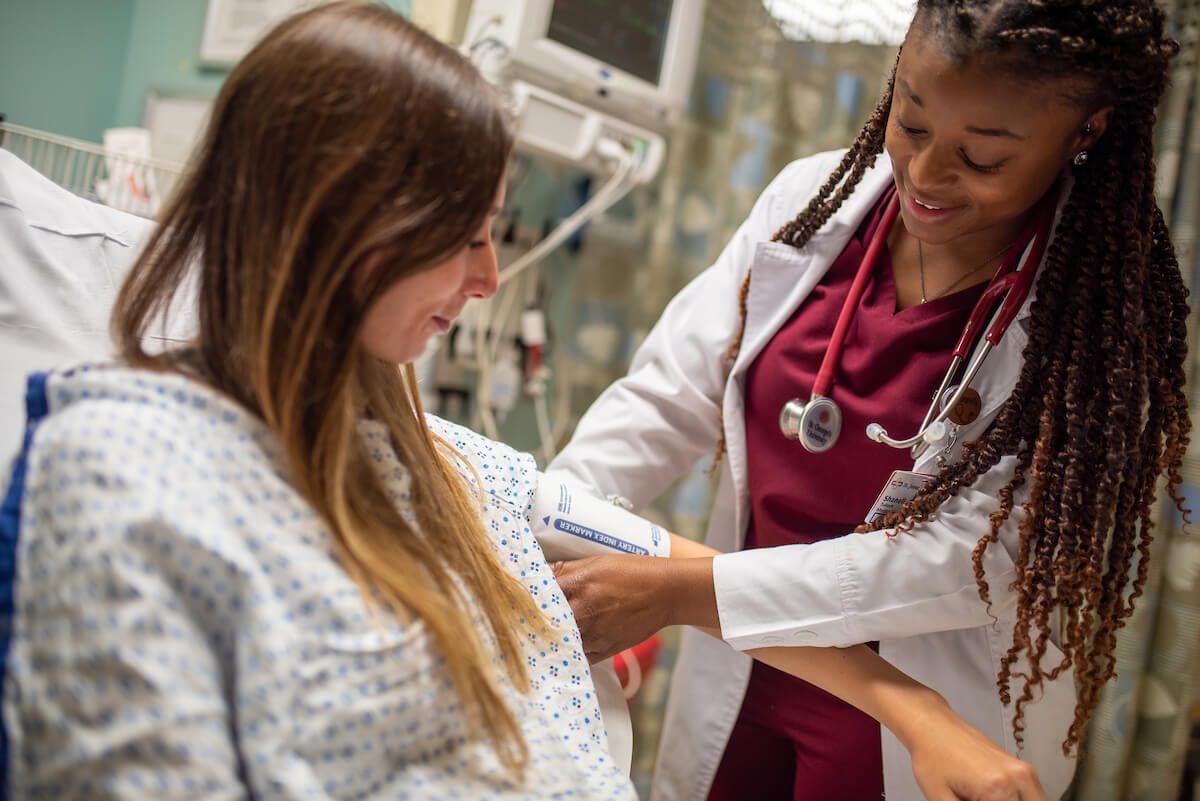

Extensive Clinical Training Network

Support Every Step of the Way

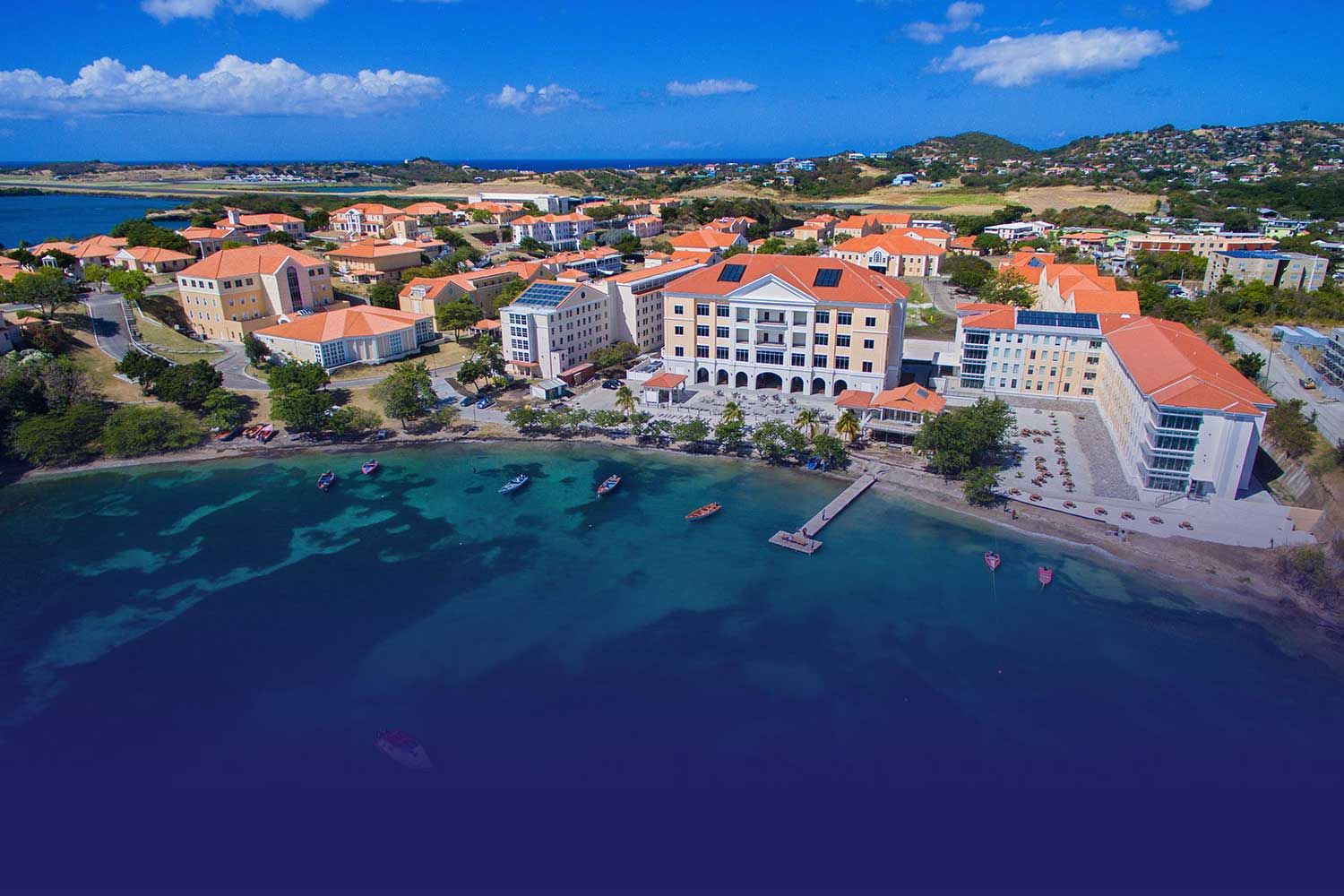
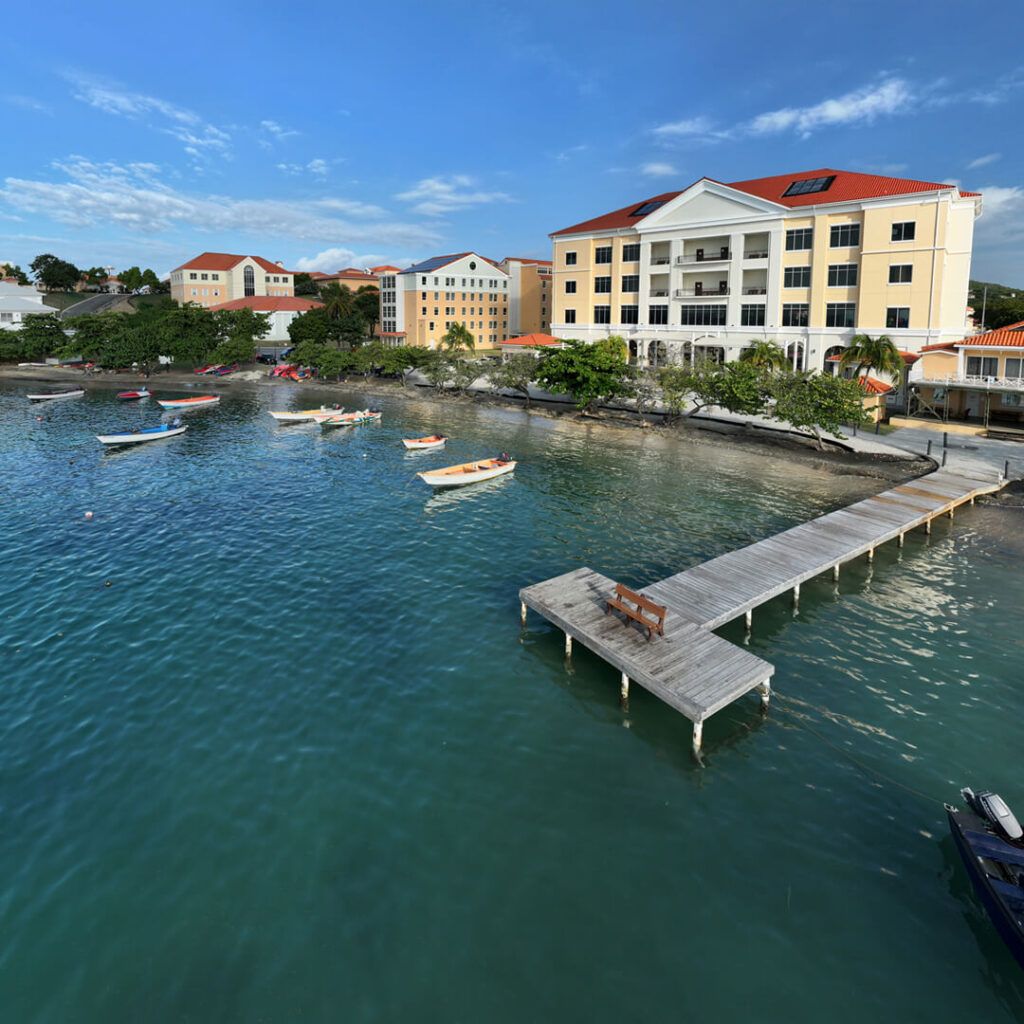
A Campus Built for Academic Excellence

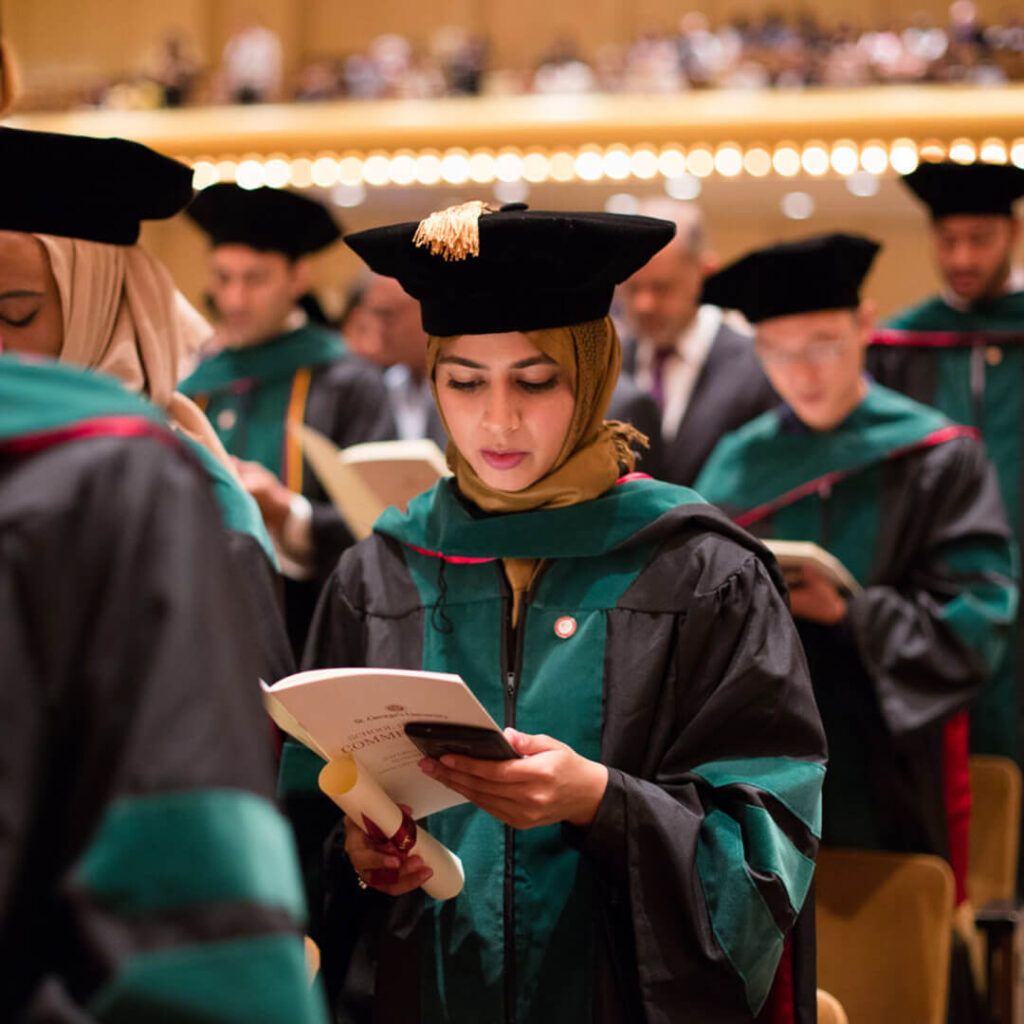
A Legacy of Excellence
5) Based on the number of students who have completed the Doctor of Medicine program from 1981-2025.
From Dr.eam To Doctor
Learn more about our MD program and tracks
Every aspect of our MD program and tracks are intentionally designed to support you on your path to becoming a physician.
Flexible Start Dates: Choose from multiple entry terms in April, August, or January to begin your medical education at your convenience.
Average of 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 and 2024 residency placement rates. Residency placement rate is defined as the total number of students/ graduates who obtained a US residency divided by the total number of students / graduates who applied to a US residency program in a given year as of October 2024.
Program and Track Highlights
- Global Recognition: SGU’s School of Medicine has been continuously accredited for decades, enabling our students to be eligible to practice in the US.
- Clinical Training: 85+ hospitals and health systems in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom offer clinical and ambulatory training and support
- Legacy of Excellence: Join the network of over 25,000 graduates* who have impacted healthcare worldwide.
*Based on the number of students who have completed the Doctor of Medicine program from 1981-2025.

Connect With Us.
- Learn more about our MD program and tracks
- Receive priority invitations to our prospective student events
We will be in touch soon, but if you have questions now, email us at admissions@sgu.edu







